Hybrid cloud architecture is a popular buzzword in the IT industry today. It has become an essential part of modern computing, enabling businesses to leverage the best of both worlds, public and private cloud infrastructures. In this article, we will explore what hybrid cloud architecture is, how it works, its benefits, and some common misconceptions about it.
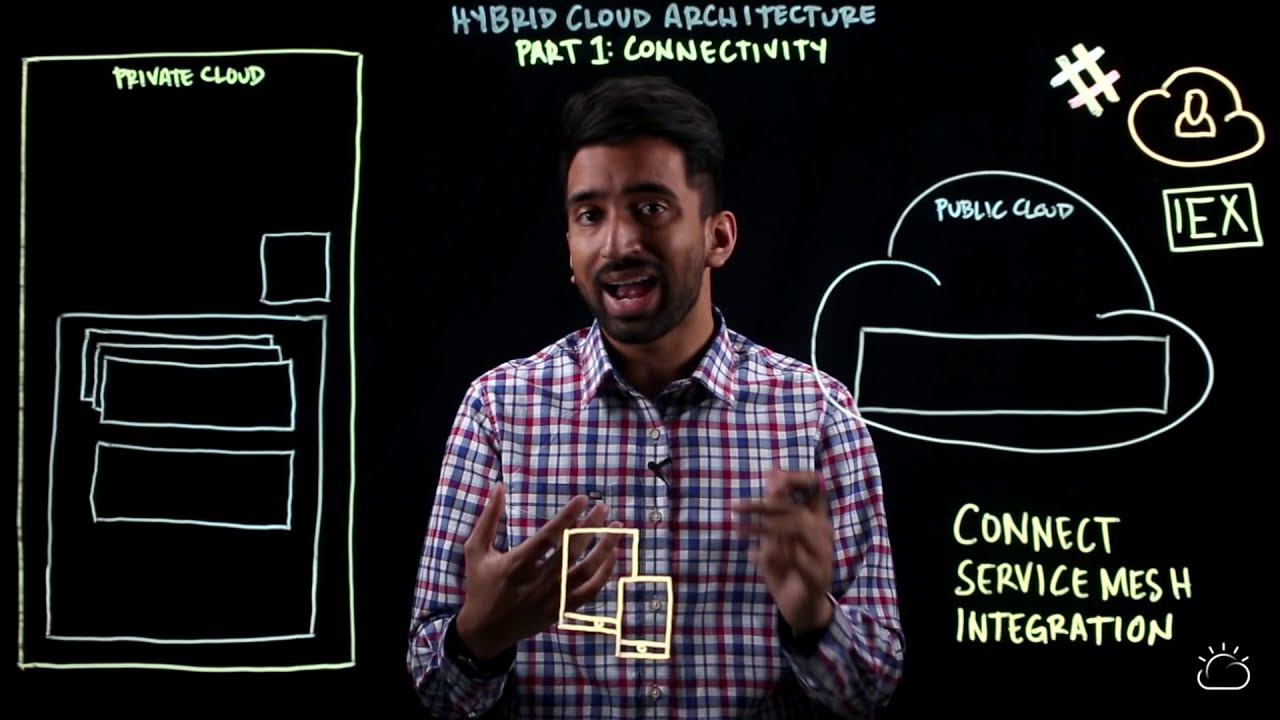
Hybrid cloud architecture is a computing environment that combines two or more distinct types of cloud services, usually public and private clouds, interconnected by secure networking protocols. This combination allows organizations to utilize the advantages of both cloud models while mitigating their limitations by providing a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for managing workloads and data.
The private cloud infrastructure provides a dedicated environment, mainly used for sensitive workloads that require high levels of security, compliance, and customization. Meanwhile, public cloud infrastructure is a shared environment operated by third-party providers, offering on-demand resources, higher scalability, and lower cost. By combining these environments, organizations can optimize their workload distribution based on their needs and budget, ensuring better performance, availability, and cost-efficiency.
Most organizations are at the least experimenting with cloud workloads, however many even have a really combined cloud surroundings. Of the organizations working cloud workloads, we estimate at the least 80 % have a multi-cloud surroundings that features entry to each on-prem and public cloud cases, in addition to utilizing a number of suppliers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google, Oracle, IBM, SAP, and many others.). This makes the world of cloud deployments very complicated.

To implement hybrid cloud architecture, organizations must have a solid understanding of their business requirements, application dependencies, and data classification. They need to define which workloads are suitable for each environment and establish secure connectivity between them.
There are various ways to connect the private and public cloud components, such as VPN (virtual private network), direct connection, or inter-cloud networking tools. Once connected, organizations can use several strategies to manage their workloads, such as load balancing, auto-scaling, and disaster recovery.
One of the most significant advantages of hybrid cloud architecture is the flexibility it provides, allowing organizations to change their workload distribution, size, and location based on their business needs. It also enables them to leverage different cloud providers’ unique advantages, such as region-specific compliance or specialized services.

Hybrid cloud architecture offers numerous benefits to organizations that adopt it. Some of these include:
By combining public and private clouds, organizations can optimize their workload distribution, ensuring better performance, availability, and cost-efficiency.
Organizations can save significant costs by utilizing the pay-as-you-go model of public cloud for non-sensitive applications while using a private cloud for critical workloads.
The private cloud environment provides dedicated resources, which are more secure and compliant than public cloud environments. Organizations can also customize their security protocols according to their specific needs.
Hybrid cloud infrastructure enables organizations to take advantage of both public and private clouds’ backup and recovery capabilities, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime in case of failure.
Organizations can quickly respond to changing business requirements by leveraging the flexibility and scalability of hybrid cloud architecture. It enables them to scale up or down their workloads efficiently without affecting their performance, availability, or security.

Despite its wide adoption and numerous benefits, hybrid cloud architecture still faces some misconceptions. Here are some common misconceptions and the truths behind them:
While implementing hybrid cloud architecture requires initial investment, it helps save significant operational costs in the long run, compared to traditional IT infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud architecture provides better security and compliance than public cloud environments and allows organizations to customize their security protocols based on their specific needs.
Implementing hybrid cloud architecture may require some additional management efforts, but it provides better control and flexibility over the IT infrastructure, enabling organizations to manage their workloads efficiently.
To utilize hybrid cloud architecture, organizations must first assess their business requirements, workload distribution, and data classification. They can then identify which workloads are suitable for a private or public cloud environment and establish secure connectivity between them.
There are various tools and services available in the market that can simplify this process and provide better workload management, security, and compliance. Using these tools, organizations can optimize their costs, performance, and availability of their IT infrastructure.
Several companies have already implemented hybrid cloud architecture successfully. Here are some examples:
Netflix uses Amazon Web Services (AWS) for its public cloud infrastructure and Open Connect for its private cloud. This allows them to store their sensitive data in a secure, dedicated environment while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of AWS for non-sensitive workloads.
Comcast utilizes hybrid cloud architecture to support its video on-demand (VOD) service, delivering content to millions of customers globally. They use AWS for its public cloud infrastructure and an OpenStack-based private cloud for its VOD platform, providing better performance, control, and cost-efficiency.
GE implemented a hybrid cloud architecture, combining AWS for non-sensitive workloads and a private cloud for critical and sensitive applications. This enables them to optimize their workload distribution, enhance security, and improve scalability and agility.
Hybrid cloud architecture offers several advantages over traditional IT infrastructure and pure public or private clouds. Here are some key comparisons:
Hybrid cloud architecture can provide significant cost savings compared to traditional IT infrastructure, allowing organizations to utilize the pay-as-you-go model of public cloud for non-critical workloads while using a private cloud for sensitive data, reducing operational costs.
Hybrid cloud architecture provides better security and compliance than public cloud infrastructures by utilizing dedicated resources and enabling customization of security protocols.
Hybrid cloud architecture provides better flexibility and scalability than traditional IT infrastructure by enabling organizations to leverage both public and private clouds’ unique advantages, optimizing their workload distribution and enhancing performance.
To implement hybrid cloud architecture successfully, organizations should consider the following advice:
Before adopting hybrid cloud architecture, organizations should assess their business needs, identify which workloads are suitable for each environment, and define their security and compliance requirements.
Organizations should plan their workload distribution based on their business needs and budget, ensuring better performance, availability, and cost-efficiency.
Implementing secure connectivity between the public and private cloud components is crucial for successful hybrid cloud adoption. Organizations must choose the right connectivity option based on their needs and ensure secure data transfer between environments.
Organizations should monitor and manage their workloads efficiently, leveraging tools and services that can simplify the process and provide better control over their IT infrastructure.
To maximize the benefits of hybrid cloud architecture, organizations should continuously review and optimize their workload distribution, security protocols, and connectivity options based on their changing business needs.
Public cloud infrastructure is a shared environment operated by third-party providers, offering on-demand resources, higher scalability, and lower cost. Meanwhile, private cloud infrastructure provides dedicated resources, primarily used for sensitive workloads that require high levels of security, compliance, and customization.
Hybrid cloud infrastructure enables organizations to take advantage of both public and private clouds’ backup and recovery capabilities, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime in case of failure.
Implementing hybrid cloud architecture requires initial investment, but it helps save significant operational costs in the long run compared to traditional IT infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud architecture provides better security and compliance than public cloud environments and allows organizations to customize their security protocols based on their specific needs.
Organizations can leverage various tools and services available in the market that can simplify workload management, security, and compliance for hybrid cloud environments.
Hybrid cloud architecture is a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for managing workloads and data in modern computing environments. It enables organizations to optimize their workload distribution based on their business needs, while leveraging the unique advantages of both public and private cloud infrastructures. By following best practices and continuously optimizing their hybrid cloud architecture, organizations can maximize its benefits and gain a competitive advantage in the market.