
Hybrid integration is a term that refers to the process of integrating different systems, applications, and data sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure. It combines both on-premises and cloud-based solutions to enable seamless data flow across various platforms, applications, and endpoints. Hybrid integration is becoming increasingly popular among organizations due to its ability to combine the best of both worlds: the flexibility of cloud computing and the security of on-premises solutions.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of hybrid integration, exploring what it is, how it works, and its benefits. We’ll also provide examples, comparisons, and advice for those looking to implement hybrid integration solutions in their organizations.

Hybrid integration is the process of integrating multiple systems, applications, and data sources across on-premises and cloud-based environments. The integration involves connecting different systems, applications, and data to create an integrated environment that can share data seamlessly across various endpoints.
Rearchitecting for the cloud ought to embrace containerization of main software elements in one thing like Docker, which may then be managed by an open sourced Kubernetes orchestration framework for optimization of assets and effectivity. We anticipate that containerization will finally be the defacto normal for working workloads within the cloud, and never simply the wrapped up monolithic app implementations introduced over from consumer server implementations.
With the advent of cloud computing, many organizations have been migrating some or all of their IT infrastructure to the cloud. However, this has created a challenge when it comes to integrating their existing on-premises systems with cloud-based solutions. Hybrid integration addresses this challenge by providing a way to integrate both on-premises and cloud-based environments.
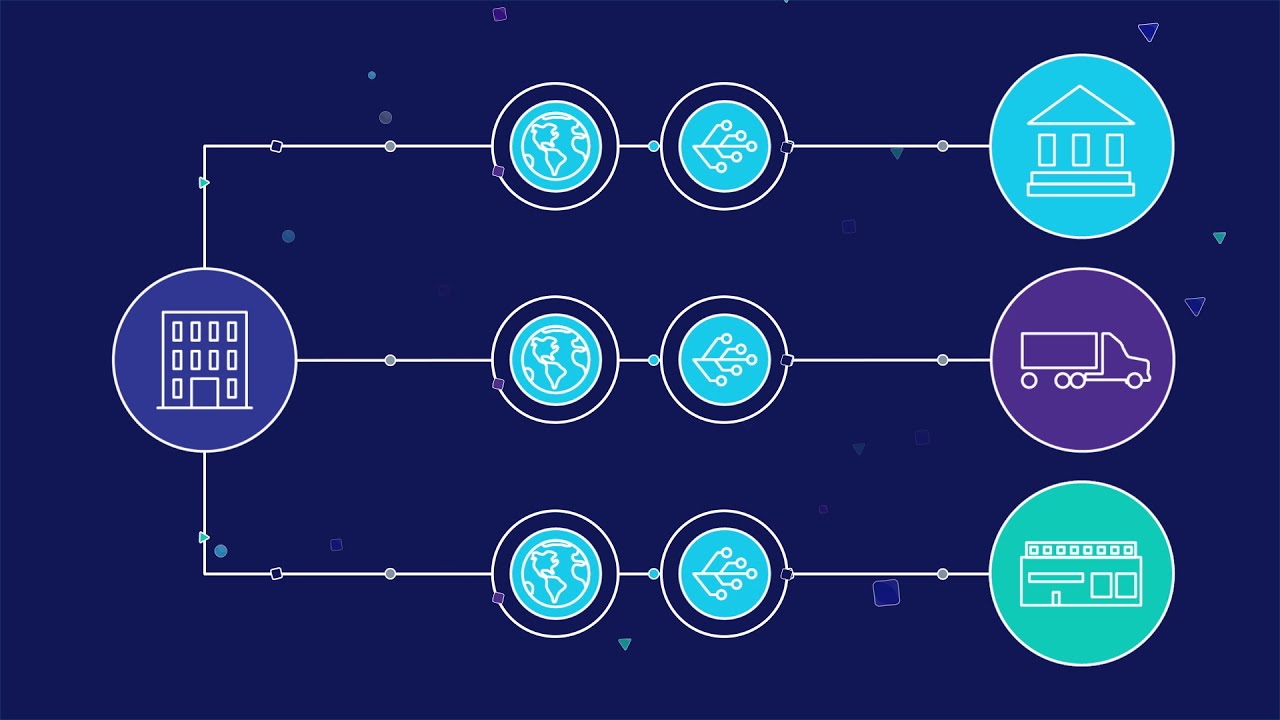
Hybrid integration solutions typically involve a middleware layer that connects different systems, applications, and data sources. The middleware layer acts as a bridge between the on-premises and cloud-based solutions, enabling them to communicate with each other seamlessly.
The middleware layer may use different integration technologies such as API management, messaging, event-driven architectures, and microservices. These technologies help to manage the flow of data between different systems and applications, ensuring that data is delivered securely and efficiently.
Hybrid integration solutions also provide monitoring and management capabilities to ensure that data is flowing smoothly across the integrated environment. This helps to identify and address any issues that may arise, ensuring that the integrated environment is always up and running.

Hybrid integration solutions provide several benefits to organizations, including:
Hybrid integration solutions allow organizations to have the flexibility of cloud computing while still maintaining the security and control of on-premises systems. This enables organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud computing without compromising on security and compliance requirements.
Hybrid integration solutions are scalable, allowing organizations to add or remove resources as needed. This enables organizations to handle varying workloads and spikes in demand without having to invest in additional hardware or software.
Hybrid integration solutions can be cost-effective, as they allow organizations to use existing on-premises resources alongside cloud-based solutions. This reduces the need for large capital investments in new hardware and software, making it an attractive option for organizations with limited budgets.
Hybrid integration solutions enable organizations to share data seamlessly across different systems and applications, improving collaboration between teams. This can lead to increased productivity and efficiency, as teams can access the data they need when they need it.

Here are some examples of hybrid integration in action:
An e-commerce company may use a hybrid integration solution to connect its on-premises order management system with its cloud-based e-commerce platform. This enables the company to fulfill orders more efficiently and track inventory levels in real-time.
A healthcare organization may use a hybrid integration solution to integrate patient data from various sources, such as electronic medical records (EMRs), medical imaging systems, and diagnostic testing equipment. This enables healthcare providers to make better-informed decisions about patient care, leading to improved health outcomes.
A manufacturing company may use a hybrid integration solution to connect its on-premises supply chain management system with its cloud-based logistics platform. This enables the company to manage inventory levels more efficiently and track shipments in real-time.
Here are some comparisons between hybrid integration and other integration solutions:
On-premises integration involves integrating systems and applications within an organization’s data center. While this approach provides greater control and security, it may be less flexible and scalable than hybrid integration solutions. On-premises integration also requires a significant investment in hardware and software.
Cloud-based integration involves integrating systems and applications using cloud-based middleware solutions. While this approach can be highly scalable and cost-effective, it may not provide the same level of control and security as hybrid integration solutions. Cloud-based integration solutions also require a reliable internet connection, which may not be available in all locations.
Here are some tips for organizations looking to implement hybrid integration solutions:
Before implementing any integration solution, it’s important to define your integration goals. What do you want to achieve through integration solutions? What are the specific systems, applications, and data sources that need to be integrated? Defining your integration goals will help you determine the best approach to take and ensure that you’re not wasting time and resources on unnecessary integrations.
There are many different hybrid integration technologies available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. It’s important to choose a technology that aligns with your organization’s needs and goals. Consider factors such as scalability, security, ease of use, and cost when evaluating different hybrid integration solutions.
Implementing a hybrid integration solution requires careful planning. You’ll need to consider factors such as system compatibility, data mapping, and security requirements. It’s also important to plan for contingencies and have a backup plan in case something goes wrong during the implementation process.
Before deploying any hybrid integration solution, it’s important to test it thoroughly. This will help you identify and address any issues before they become major problems. Testing should include both functional testing (ensuring that the solution works as intended) and performance testing (ensuring that the solution can handle the expected workload).
Once your hybrid integration solution is up and running, it’s important to monitor and maintain it regularly. This will help you identify and address any issues that may arise, ensuring that the solution continues to work smoothly over time. Regular maintenance tasks may include upgrading software, monitoring system logs, and applying security patches.
Hybrid integration involves integrating multiple systems and applications across on-premises and cloud-based environments, while API integration specifically refers to the use of APIs (application programming interfaces) to connect different systems and applications.
Hybrid integration enables teams to share data seamlessly across different systems and applications, improving collaboration and streamlining workflows. This can lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
Some challenges of implementing hybrid integration solutions include system compatibility, data mapping, security requirements, and the complexity of the integration process.
Hybrid integration can improve data security by providing organizations with greater control over their data. However, it’s important to ensure that all data transfers are encrypted and that proper security protocols are in place at all times.
Yes, hybrid integration can be a good fit for small businesses, particularly those with limited budgets or IT resources. Hybrid integration allows small businesses to take advantage of cloud computing while still maintaining control over their on-premises systems.
Hybrid integration is a powerful solution that enables organizations to integrate their on-premises and cloud-based systems and applications seamlessly. It provides flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive option for organizations of all sizes and industries. By following best practices and choosing the right hybrid integration technology, organizations can unlock the full potential of their IT infrastructure and improve collaboration and productivity across teams and departments.