In today’s fast-paced business environment, the importance of MDM master data management cannot be overemphasized. With businesses handling an enormous amount of data on a daily basis, maintaining accurate and reliable data is crucial for success. MDM master data management is the process of creating and managing a single, consistent view of an organization’s critical data assets. This article will delve into the various aspects of MDM master data management, including how to use it, examples, comparisons, and advice for businesses.
How to Use MDM Master Data Management
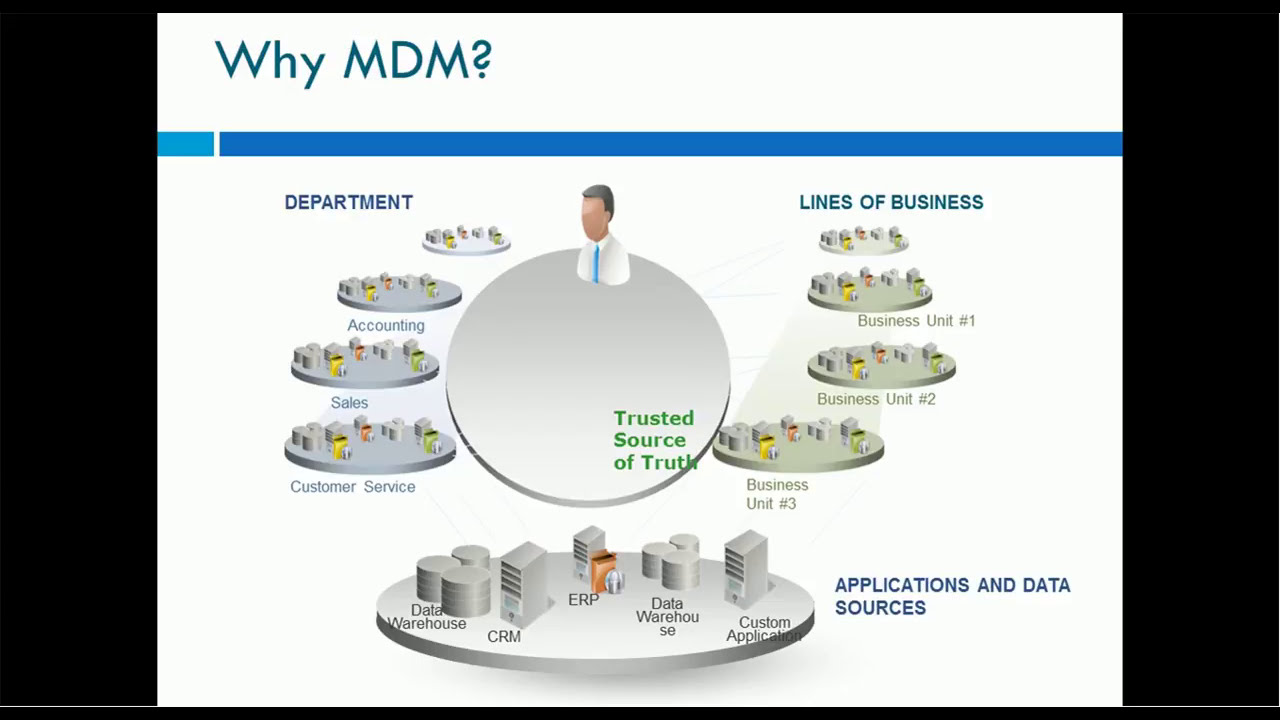
MDM master data management involves several steps that ensure the accuracy and consistency of an organization’s data. Here are some common steps involved in implementing MDM:
- Identify critical data elements: The first step in MDM is to identify the most critical data elements within the organization. These elements may include customer data, product data, financial data, or any other data that is essential to the business.
- Establish data governance: In order to manage data effectively, organizations need to establish clear data governance policies and procedures. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, setting data quality standards, and establishing data stewardship processes.
- Create a master data repository: Once the critical data elements have been identified, the next step is to create a master data repository. This repository serves as a centralized location for all master data and provides a single source of truth for the organization.
- Implement data quality controls: To ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data, organizations need to implement data quality controls. This may include data profiling, data cleansing, and data enrichment.
- Integrate with other systems: Finally, the master data repository needs to be integrated with other systems within the organization. This ensures that all systems are using the same consistent data, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
Examples of MDM Master Data Management
MDM master data management has become an essential component for businesses in various industries. Here are some examples of how MDM is being used in today’s business world:
Whereas a lot hype has been produced concerning the speedy tempo of enterprise cloud deployments, in actuality we estimate lower than 25 % of enterprise workloads are at the moment being run within the cloud. That doesn’t negate the significance of the expansion of cloud computing – however it does set some parameters round simply how prevalent it at the moment is, and the way troublesome it's to maneuver enterprise workloads to a cloud structure.
- Retail: A retail organization may use MDM to manage its product data, ensuring that all product information is accurate and consistent across all sales channels.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, MDM can be used to manage patient data, ensuring that all patient information is up-to-date and accurate, reducing the risk of medical errors.
- Financial services: Financial institutions use MDM to manage their customer data, ensuring that customer information is accurate and consistent across all systems, and complying with regulatory requirements.
Comparisons with Other Data Management Techniques
While there are many different data management techniques available, MDM offers several distinct advantages over other approaches. Here are some key comparisons:
After years of shifting functions to the general public cloud, enterprises understand it’s not the proper match for each app and are pulling a few of them again to personal clouds, forcing the companies to undertake a hybrid technique. Nevertheless it’s not a straightforward course of and one which will require formal coaching and certifications for the IT professionals tasked with this essential transition.
- MDM vs. Data Warehousing: While data warehousing is focused on storing large volumes of data for analysis purposes, MDM is focused on creating a single, consistent view of an organization’s critical data assets.
- MDM vs. Data Governance: While data governance establishes policies and procedures for managing data, MDM goes beyond governance by providing a centralized repository for master data and implementing data quality controls.
- MDM vs. Data Integration: While data integration focuses on connecting different systems and applications, MDM ensures that all systems are using the same consistent data, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
Advice for Businesses Regarding MDM Master Data Management
Implementing MDM master data management is a complex process that requires significant investment in time, resources, and expertise. Here are some tips for businesses considering MDM:
- Start small: Implementing MDM for all critical data elements at once can be overwhelming. Start small by identifying the most critical data elements and building from there.
- Get buy-in from stakeholders: MDM involves various stakeholders, including IT, business units, and data stewards. It’s essential to get buy-in from all stakeholders to ensure the success of the project.
- Focus on data quality: MDM is only effective if the data is accurate and reliable. Implementing data quality controls such as data profiling, data cleansing, and data enrichment is crucial for success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MDM master data management is an essential component for businesses that want to maintain accurate and consistent data. By following the steps outlined in this article, businesses can implement MDM effectively and reap the benefits of having a single, consistent view of their critical data assets.
Automation is a key driver in Ceridian's general cloud imaginative and prescient and technique. "It is actually the muse and the basic step that is required as an entry for us to have the ability to show out our idea," says Alan Segal, Ceridian's senior vp of enterprise know-how. "It is important within the sense that we're driving towards push-button solutioning."
Automation permits groups to concentrate on significant jobs as a substitute of on routine, repetitive duties. Whereas getting crew members onboard with automation requires a while and convincing, Segal says he has encountered little opposition to the know-how. "Getting groups to actually settle for and perceive the worth and the profit...hasn't been a big problem," he says.
Automation helped Ceridian deal with modifications that the COVID-19 pandemic dropped at its operations, for instance. "The power to handle your whole operation remotely from wherever you might be, as a result of you do not have to fret about your campus, is an important step," Perlman says. Due to its automation instruments, Ceridian was in a position to transition, nearly instantly, to 100% distant operation. "There was no downtime, and no impression to our clients as a result of we ready," he says.