As businesses increasingly rely on cloud computing to support their operations, many are faced with the decision of whether to use a public or private cloud solution. Both options offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these differences is essential for making an informed choice.
In this article, we will explore the differences between public and private clouds, their pros and cons, and how to choose the best option for your business needs.
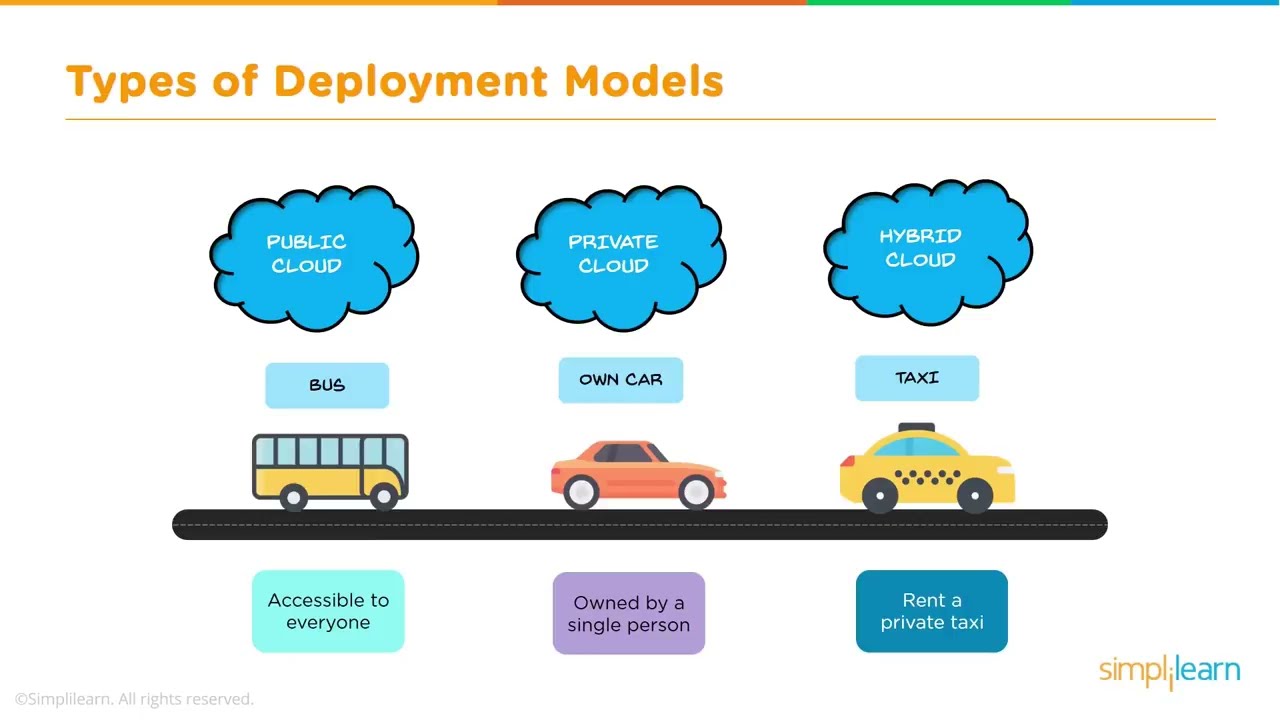
What is a Public Cloud?
A public cloud is a type of cloud service that is hosted by third-party providers and made available to the general public over the internet. Examples of public cloud services include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Rearchitecting for the cloud ought to embrace containerization of main software elements in one thing like Docker, which may then be managed by an open sourced Kubernetes orchestration framework for optimization of assets and effectivity. We anticipate that containerization will finally be the defacto normal for working workloads within the cloud, and never simply the wrapped up monolithic app implementations introduced over from consumer server implementations.
In a public cloud environment, multiple users share resources such as storage, computing power, and networking infrastructure. This makes it an affordable and scalable option for small and medium-sized businesses, as they only pay for what they need and can easily increase or decrease their usage as required.
With certifications accessible from distributors like Microsoft, NetApp, and Crimson Hat, in addition to third events such because the Cloud Certificates Council and International Data, IT professionals have loads of alternatives to pursue focused coaching within the hybrid cloud.
Lynne Williams, professor on the College of Enterprise and Data Expertise at Purdue College International, which incorporates instruction on hybrid cloud in its cyber safety and IT grasp's diploma applications, says coaching and certification are important for bigger organizations and those who fall beneath regulatory oversight.
What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud, on the other hand, is a cloud infrastructure that is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider, but its resources are not shared with other users.
Private clouds offer more control and security than public clouds, as organizations can customize their infrastructure to meet their specific requirements and have full control over data access and management. However, they also require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Community virtualization has additionally drastically improved Ceridian's safety panorama, Perlman says. "Above and past your typical layered safety method, network virtualization places you in a significantly better place to guard the information that you just're charged with securing on behalf of your clients," he says.
"There are a number of major benefits that we're trying to benefit from in community virtualization," says Kevin Younger, principal engineer for Ceridian's Dayforce. Initially is safety and microsegmentation."
Ceridian is utilizing VMware's NSX-T to allow microsegmentation, which provides extra granular safety controls for better assault resistance. It is a rigorous method, and it requires time-consuming evaluation and planning to get it proper. "We begin with a zero belief method within the very starting," Younger explains. "This forces us to know our utility nicely, and in addition forces us to correctly doc and open solely the holes required for the applying, safety being firstly."
When to Choose a Public Cloud
There are several scenarios where a public cloud may be the best option for a business:
- Cost-effectiveness: Public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing businesses to save money by only paying for the resources they use.
- Ease of scalability: Public clouds can quickly scale up or down in response to changing business needs, making them ideal for businesses with fluctuating demand.
- Access to cutting-edge technology: Public cloud providers often offer the latest technology and features, which may not be available to organizations with limited resources.
When to Choose a Private Cloud
While public clouds offer many benefits, there are also situations where a private cloud may be a better fit:
- Data security and compliance: Organizations that deal with sensitive data or have strict regulatory requirements may prefer the added security and control of a private cloud.
- Customization and flexibility: Private clouds allow businesses to customize their infrastructure to meet their specific needs and integrate with existing on-premises systems.
- Predictable costs: Unlike public clouds, which charge based on usage, private clouds offer predictable costs that can help businesses better manage their budgets.
Pros and Cons of Public Clouds
Pros
- Cost-effectiveness: Public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing businesses to save money by only paying for the resources they use.
- Scalability: Public clouds can quickly scale up or down in response to changing business needs, making them ideal for businesses with fluctuating demand.
- Reduced maintenance: Public cloud providers handle hardware and software maintenance, eliminating the need for businesses to maintain their own IT infrastructure.
Cons
- Security risks: Public clouds can pose security risks as they are accessed over the internet and shared with other users.
- Lack of control: Public clouds are managed by third-party providers, limiting the level of control that businesses have over their infrastructure and data.
- Downtime and performance issues: Public clouds are susceptible to downtime and performance issues, which can impact business operations.
Pros and Cons of Private Clouds
Pros
- Greater control and security: Private clouds offer greater control and security than public clouds, as businesses have full control over their infrastructure and data.
- Customization and flexibility: Private clouds allow businesses to customize their infrastructure to meet their specific needs and integrate with existing on-premises systems.
- Increased reliability: Private clouds can provide better uptime and performance than public clouds, as resources are not shared with other users.
Cons
- High upfront costs: Private clouds require significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and personnel costs.
- Maintenance and management: Private clouds require ongoing maintenance and management, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Limited scalability: Private clouds may be more difficult to scale up or down than public clouds, making them less suitable for businesses with fluctuating demand.
Alternatives to Public and Private Clouds
While public and private clouds are the most common cloud computing options, there are several alternative solutions that businesses may want to consider:
- Hybrid cloud: A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing businesses to take advantage of both options while maintaining control over their data and infrastructure.
- Community cloud: A community cloud is a shared cloud environment that is used by multiple organizations with similar requirements, such as those in the same industry or geographic location.
- Multi-cloud: A multi-cloud strategy involves using multiple cloud providers to meet different business needs. This approach can increase flexibility and reduce the risk of vendor lock-in.
How to Choose Between Public and Private Clouds
Choosing between public and private clouds requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Security and compliance: Organizations with strict security and compliance requirements may prefer the added control and security of a private cloud.
- Cost: Businesses with limited budgets may find the pay-as-you-go model of public clouds more cost-effective than the upfront investment required for a private cloud.
- Scalability: Companies with fluctuating demand may benefit from the scalability offered by public clouds.
- Customization: Organizations that require customized infrastructure may prefer the flexibility and customization options of a private cloud.
- Uptime and performance: Businesses that require high uptime and performance may opt for a private cloud.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the specific needs and goals of each organization.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between public and private clouds?
Public clouds are hosted by third-party providers and shared among multiple users, while private clouds are dedicated to a single organization and offer greater control and security.
2. Are public clouds less secure than private clouds?
Public clouds can pose security risks as they are accessed over the internet and shared with other users. However, public cloud providers have strict security measures in place to mitigate these risks.
3. Can businesses use both public and private clouds?
Yes, some organizations use a hybrid cloud approach that combines both public and private clouds to meet their business needs.
4. Is it more cost-effective to use a public or private cloud?
The answer depends on the specific needs and usage patterns of each organization. Public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, while private clouds require significant upfront investment but can provide predictable costs over time.
5. Can private clouds be hosted by third-party providers?
Yes, some businesses choose to have their private clouds hosted by third-party providers for added convenience and support.
Conclusion
Choosing between public and private clouds requires careful consideration of several factors, including security, cost, scalability, customization, and uptime. While both options offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, there are also alternative solutions such as hybrid clouds and multi-cloud strategies that businesses may want to consider.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the unique needs and goals of each organization. By understanding the differences between public and private clouds, businesses can make informed decisions that help them maximize the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing risks and costs.